Effective emissions intensity
Consume energy when grid intensity is lowest
The emissions intensity of the grid varies instantaneously, as both fossil fuel and renewable generators come online, ramp up and down. Reported emissions from grid-sourced electricity are generally a weighted average of all generation sources. Ideally, we would like to consume energy services when the grid emissions intensity is lowest. While this emissions arbitrage may not be recognised in your reportable emissions, these actions indirectly support renewables and facilitate the transition away from high emissions energy sources.
Deepwater can assist by aligning your site’s energy consumption with renewable availability and lowest grid emissions intensity. This can be achieved through smart control of energy storage technologies, load shifting and appliance control. Any load shifting is undertaken in close consultation with site operators, as every site is unique in which loads and processes can be rescheduled and reconfigured.
The term grid emissions intensity refers to the emissions intensity of electricity imported from the grid. The effective emissions intensity is the total emissions required to meet total demand, which may include on-site generation. Both metrics are consumption-weighted. Deepwater integrates with AEMO APIs for real time emissions intensity data. This allows Deepwater to forecast the likely emissions intensity in the near future, and manage on site renewables and battery storage to minimise the effective emissions intensity.
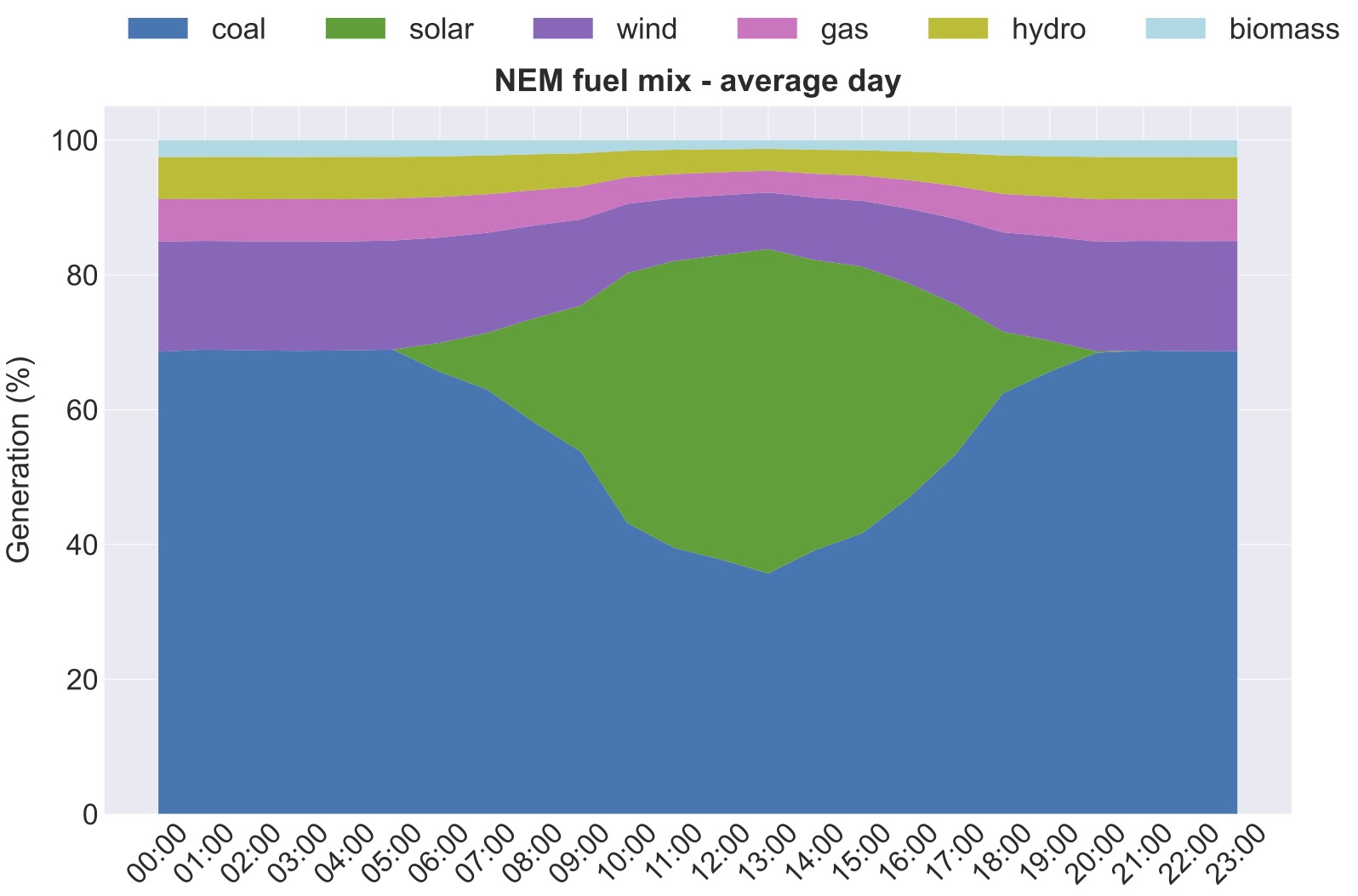
National Energy Market (NEM) data is available to determine the instantaneous or historical emissions intensity of electricity consumption.
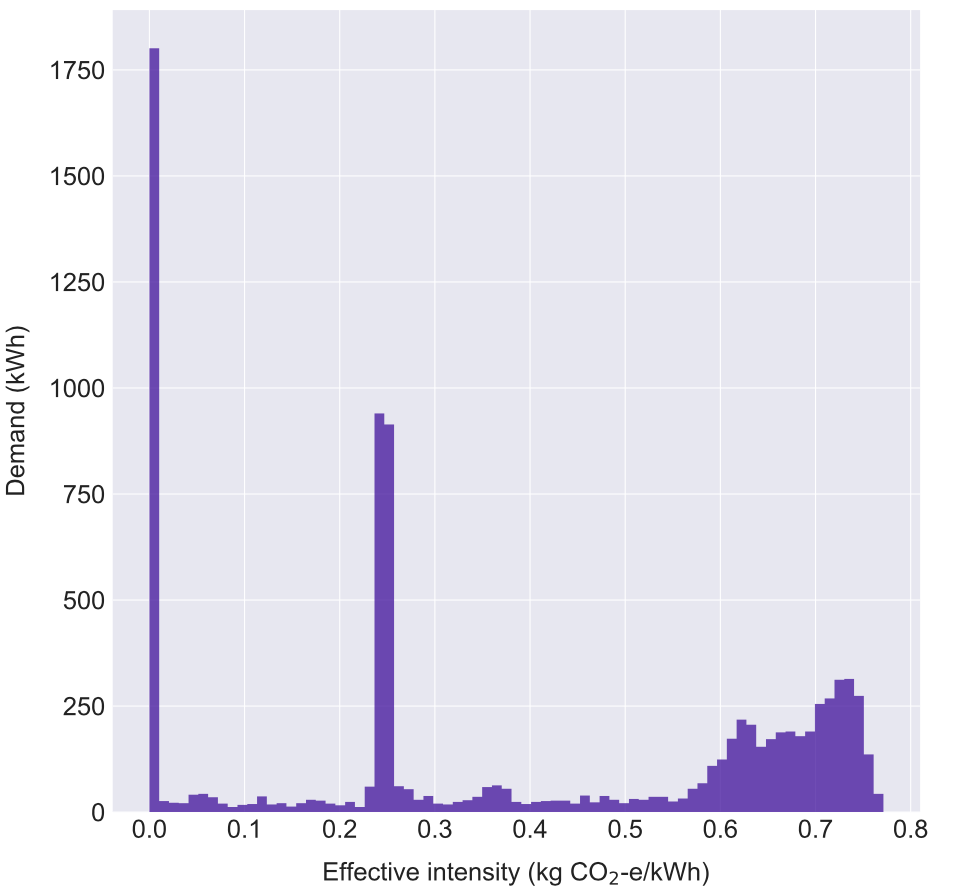
Emissions intensity usually varies, though we can aim to consume electricity when the lowest emissions sources are online.

Photo by unsplash.com/@fl__q